Atmospheric component
The atmospheric component is a two-layer quasi-geostrophic (QG) atmosphere in the beta-plane approximation. The atmospheric component is an extension of the QG model, first developed by [AC-CS80] and further refined by [AC-RP82] and [AC-CT87].
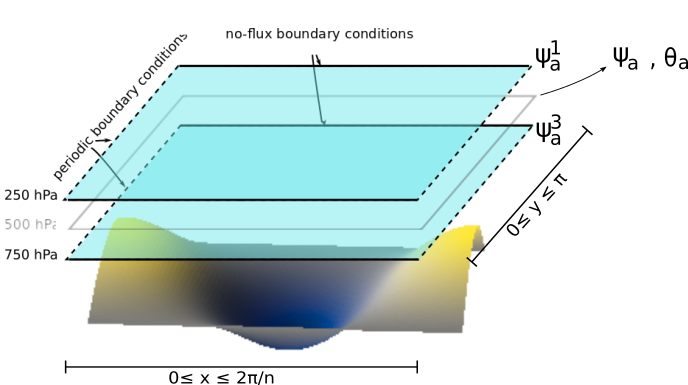
Sketch of the atmospheric model layers with a simple orography. The domain (\(\beta\)-plane) zonal and meridional coordinates are labeled as the \(x\) and \(y\) variables.
The equations of motion for the atmospheric streamfunction fields \(\psi^1_\text{a}\) at 250 hPa and \(\psi^3_\text{a}\) at 750 hPa, and the vertical velocity \(\omega = \text{d}p/\text{d}t\), read
where \(\nabla^2\) is the horizontal Laplacian.
The Coriolis parameter \(f\) is linearized around a value \(f_0\) (f0) evaluated at
latitude \(\phi_0\) (phi0_npi), \(f = f_0 + \beta y\), with
\(\beta=\text{d}f/\text{d}y\) (beta). The parameter \(k'_d\)
(kdp) quantify the friction between the two atmospheric layers,
and \(\Delta p = 500\) hPa (deltap) is the pressure difference between the atmospheric layers.
Finally, \(J\) is the Jacobian \(J(S, G) = \partial_x S\, \partial_y G - \partial_y S\, \partial_x G\).
References
- AC-CT87
P. Cehelsky and K. K. Tung. Theories of multiple equilibria and weather regimes - A critical reexamination. Part II: Baroclinic two-layer models. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 44(21):3282–3303, 1987. URL: https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0469(1987)044%3C3282:TOMEAW%3E2.0.CO;2.
- AC-CS80
J. Charney and D. Straus. Form-drag instability, multiple equilibria and propagating planetary waves in baroclinic, orographically forced, planetary wave systems. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 37(6):1157–1176, 1980. URL: https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0469(1980)037%3C1157:FDIMEA%3E2.0.CO;2.
- AC-RP82
B. Reinhold and R. Pierrehumbert. Dynamics of weather regimes: quasi-stationary waves and blocking. Monthly Weather Review, 110:1105–1145, 1982. URL: https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0493(1982)110%3C1105:DOWRQS%3E2.0.CO;2.